In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, telecommunication companies are embracing cloud migration as a strategic move to enhance their operations, increase flexibility, and unlock new possibilities. Telco cloud migration, however, brings with it a set of challenges and opportunities that demand careful consideration. In this blog, we delve into the challenges that organizations must overcome, discuss key considerations for a successful migration, and highlight the evolution of the Network Operation Centre (NOC) in the era of the Telco cloud.
Telco Cloud Migration: Capitalize on the Hybrid Existence
When companies migrate to the cloud, they will likely operate in a hybrid model for a considerable amount of time. During this transition, Telcos can reap numerous benefits, including reducing costs and increasing flexibility.
- Agility with Control: A hybrid model leverages the scalability and agility of the cloud while retaining control over critical on-premises systems.
- Cost Optimization: Telcos can select the cloud for peak (or variable) workloads and on-premises resources for stable, predictable workloads to reduce infrastructure expenses.
- Data Sovereignty and Compliance: Organizations can keep sensitive data and applications on their own private, on-premises environment without losing the speed and other benefits of the cloud.
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery: Telcos can implement robust disaster recovery plans by replicating necessary data and applications to the cloud while maintaining on-premises redundancy.
- Geographic Distribution: Cloud infrastructure can be deployed across multiple geographic regions, bringing it closer to different user bases. This improves latency and performance and optimizes user experience. For instance, If the user base is spread across multiple continents, CSPs can take a multi-cloud approach by integrating Telco cloud (private cloud) and a Hyperscale Telco cloud.
Telco Cloud Migration Challenges to Overcome
Security and Compliance
In a hybrid environment, data and applications are distributed across multiple platforms and need to connect to transmit data. This expands the attack surface and requires hybrid security with additional security protocols and controls across different platforms.
Data Synchronization and Latency
Synchronizing data between on-premises and cloud systems may introduce latency and potential inconsistencies, affecting user experiences and application performance.
Vendor Lock-In
Cloud vendor lock-in may occur in case a CSP heavily depends on a specific provider (or appliance OEM), making it difficult to switch to another vendor without significant investment and effort.
Operational Overhead
Maintaining both on-premises and cloud resources requires additional operational effort for monitoring, management, and troubleshooting.
4 Principles for Overcoming Telco Cloud Migration Challenges
1. Start Small and Grow Gradually
Agile Approach: Break down the migration journey into smaller, manageable phases. Based on feedback and outcomes, make modifications by implementing agile practices for improving flexibility and adaptability during the migration process.
Risk Management: Establish a comprehensive risk assessment framework to identify potential challenges and vulnerabilities and create mitigation strategies to develop a contingency plan to address unforeseen issues.
Documentation and Knowledge Sharing: Develop standardized documentation (SOPs and MOPs) to capture the process, configurations, and troubleshooting information to address issues during migration. Conduct regular knowledge-sharing sessions with key stakeholders for better hybrid migration.
2. Upskill Current Talent (or Acquire New Talent)
Skills and Training: Every individual involved in the cloud migration project must have pre-requisite skills to turn the plan into action. CSPs should internally skill existing employees or hire cloud workers (a costlier alternative) to close the talent gap quickly. Alternatively, look for an eligible partner who can augment organizations to perform the critical migration.
Roles and Responsibilities: Large migration projects often have multiple teams with dozens of different experts. Building a responsible, accountable, consulted, informed (RACI) matrix should help define the roles and responsibilities of each team and team members. This will improve coordination between teams and address emerging issues during migration.
Stakeholder Involvement and Communication: Involving the right stakeholders in decision-making processes, implementing comprehensive change management plans, and effectively communicating the benefits of the migration can address concerns, resistance, and expectations from the project.
3. Choose Appropriate Hybrid Cloud Management Tools
Choose appropriate management tools that provide visibility, monitoring, and control across the hybrid environment. This includes cloud management platforms, monitoring solutions, and automation frameworks.
Resource provisioning and automation tools streamline resource provisioning, reduce manual intervention, and optimize resource utilization by allocating and de-allocating resources across both on-premises and cloud environments based on predefined policies, workload demands, and budget constraints.
The use of monitoring and management tools can greatly improve the ability to quickly detect and respond to issues. These tools collect and analyse data from metrics, logs, and events, and provide a unified dashboard for monitoring resource performance, health, and security across on-premises and cloud environments.
In addition, integrating DevOps and CI/CD pipelines can help streamline software development and delivery processes by automating tasks such as application deployment, testing, and scaling. This speeds up development and promotes collaboration between development and operations teams, resulting in a more efficient and error-free workflow.
4. Automation and Orchestration
It is essential to leverage automation and orchestration tools to streamline the deployment, scaling, and management of resources. This approach can significantly reduce manual intervention and the potential for human errors.
Automation plays a vital role in resource provisioning, configuration management, patch management, backup and disaster recovery management, scaling, and load balancing.
Orchestration takes automation to the next level by coordinating and managing complex workflows and processes that involve multiple tasks for application and network functions deployment, service integration, hybrid workflows, and self-service portals.
Simplify Telco Cloud Management with Next-Gen NOC
As Telcos steadily move towards the cloud, they face the risk of running an outdated NOC. Traditional NOCs will lack the monitoring and management capabilities required to detect and resolve issues related to any cloud service. To maintain control, changes are needed in three distinct areas – people, processes, and tools.
|
Category |
Traditional NOC |
Next-Gen NOC (Everything in a traditional NOC plus) |
|
People |
|
|
| Process |
|
|
|
Technology |
|
|
Let’s explore the essential NOC upgrades to manage Telco cloud operations.
- Setup service management for COTS (commercial off-the-shelf) hardware, servers, and middleware.
- Ensure the talent can adjust to the procedural changes and adapt new skills like virtualization.
- Amend existing processes to include virtualization, storage, backups, and patching nuances.
- Onboard specialized virtualization, orchestration, and automation tools.
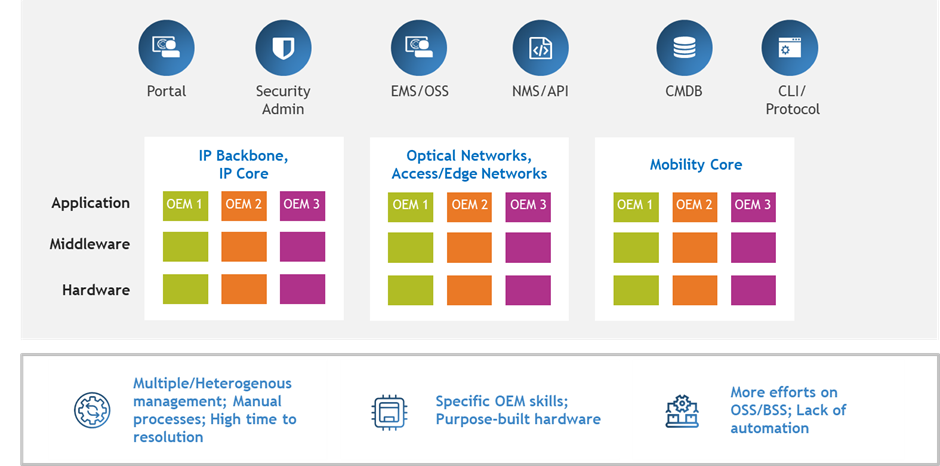
Fig. 1 – Existing CSP NOC: Multiple Network Management Panes (Siloed, Manual & Complex)
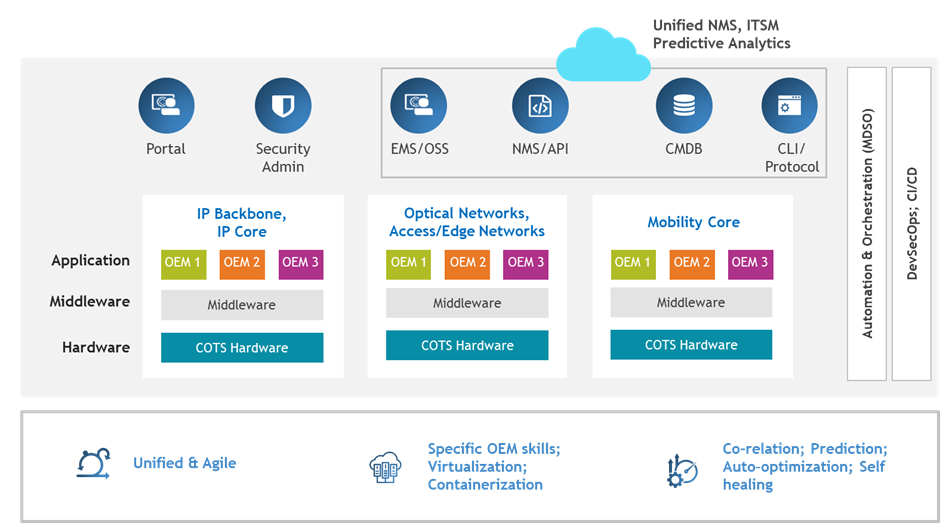
CSPs should also consider leveraging AI/ML to enhance Telco cloud operations by introducing prediction, automation, and workflows.
Fig. 2 – AI/ML Based Integrated Next-Gen NOC for Telco Cloud
These measures can help offset any additional operating costs associated with managing the cloud. For instance, Telcos can introduce the following process automation:
- Alarm Updates: Auto-alarm to ticket assignment; Auto-alarm correlation for fault identification.
- Root Cause Analysis (RCA): Automated RCA; Predictive fault – RCA recommendations.
- Network automation: Self-healing/optimizing networks; Workflow and closed loop automation based on business and network rules.
- Additional process automation: Auto resolution and closure using KMS; human task automation; automated knowledge base update; AR/VR-based field fault management; Zero-Touch automation.
In Summary
The journey to Telco cloud migration is rife with both challenges and opportunities. To successfully navigate this transformation, telcos must address security, compliance, cost, and performance concerns. By embracing a strategic approach that includes starting small, upskilling teams, and utilizing hybrid cloud management tools, telcos can optimize their cloud migration efforts. Additionally, evolving the NOC to a Next-Gen model equipped with AI/ML capabilities empowers telcos to efficiently manage the complexities of virtualized environments and ensure seamless operations.
About TCTS Cloud Services
TCTS offers a wide range of solutions for Communication Services Providers to design, deploy, and operate the Telco cloud with ease. With our decades of experience in dealing with complex operating environments, we deliver automation, security, and service assurance to address the challenges of the digital-first world.
























![Telco Cloud: A Key Enabler to Telco Transformation [Part 1]](https://www.tatacommunications-ts.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Telco-Cloud-blog_image-1-500x383.png)




