The growing trend towards increasing connectivity and communication between people and things requires reliable and stable networks. As enterprises seek more advanced, flexible, and secure connectivity solutions, 5G network slicing and private 5G networks have emerged as two powerful technologies.
Each serves distinct needs: network slicing enables virtualized segments of a public network to be tailored for different service level agreements (SLAs), while private 5G networks offer enterprises full control over their connectivity. Both options allow businesses to achieve mission-critical objectives—whether it’s ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), massive IoT connectivity, or high-speed mobile broadband.
This blog explores how enterprises can choose between network slicing and private networks based on their unique requirements, such as bandwidth, security, and geographical needs. It also examines how both technologies can be deployed simultaneously for mixed-use cases, offering a blend of flexibility and performance.
Understanding network slicing and private networks
What is network slicing?
A commercial 5G network is shared between users and may not be able to ensure ideal performance for business use cases. Network slicing divides a physical network into several virtualized slices. And each slice can be designed to undertake diverse service level agreements (SLA) regarding throughput, latency and reliability.
This means network slices can be specially designed to meet enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLC) and massive Machine-Type Communications (mMTC). These three categories are the drivers to specific services including, live broadcasting, virtual and augmented reality, automotive, healthcare, utilities, logistics and more.
Furthermore, CSPs can offer dedicated network slices to enterprises to generate new revenues. Enterprises benefit by not investing in standalone private networks while having access to new services with carrier-grade network performance.
What are private 5G networks?
A private network is designed for enterprises to utilize dedicated frequencies and provide customized networks. These custom networks allow enterprises to provide state-of-the-art services at various locations.
In essence, a private 5G network is a 5G-based local area network (LAN) that integrates 5G with other communication technologies and systems to ensure SLA and secure communication within a particular location.
Private 5G networks are garnering interest from vertical markets where companies have a highly specialized needs and large-scale operations (e.g., smart factories, smart ports, autonomous driving, etc.). They can either choose to build and maintain private networks themselves or work with CSPs, equipment providers or telecom managed service providers.
Private 5G networks or network slicing?
The selection of either a private 5G network or 5G network slicing will largely be dictated by the specific needs of the enterprise. Different use cases will map to different deployment models, with private networks offering distinct advantages for some scenarios, while network slicing may prove more appropriate in others.
| Private Network | Network Slicing |
|
|
In markets where regulators have allocated spectrum specifically for private networks, enterprise customers are more likely to opt for private network deployment. This approach grants them greater control, enhanced security, and tailored performance.
However, in regions where regulatory constraints limit the availability of private spectrum, network slicing emerges as a highly viable alternative. By leveraging advanced slicing technology, enterprises can access portions of the public network that are customized to their needs, offering flexibility without the capital investment required for a full private deployment.
Tailoring Networks to High-Bandwidth and Security Needs
For enterprises with high-bandwidth requirements—such as factories utilizing a significant number of IoT devices—private networks present a compelling option. A dedicated 5G network enables URLLC, which is a must-have for mission-critical operations. Furthermore, the ability to keep the user plane on premises ensures greater control over data, addressing stringent security and privacy concerns.
Regulatory environments also influence bandwidth availability. For instance, in Germany, an enterprise can secure up to 100 MHz of spectrum through private network deployment—significantly more than the 10 MHz typically available via public network slicing. This expanded bandwidth capacity directly impacts an enterprise’s ability to meet its connectivity needs in data-intensive environments [1].
Simplifying Deployment with Network Slicing
For enterprises seeking a less complex, more cost-effective solution, network slicing offers significant advantages. Rather than investing in the infrastructure and management of a private network, enterprises can lease a slice of the public network. This approach reduces capital expenditure and operational complexity, as network management responsibilities remain with the telecom operator.
By removing the burden of network deployment and management, enterprises can focus on accelerating device setup and driving business outcomes. This streamlined process, combined with lower costs, makes network slicing an attractive option for enterprises with simpler connectivity requirements or for those operating in markets where spectrum access is restricted.
Mixed Deployment Scenarios for Enterprises
5G provides greater performance for data-heavy applications, use cases where ultra-low latency is non-negotiable, and environments with thousands of connections. There are a few scenarios where deploying both network slicing and private networks is suitable.
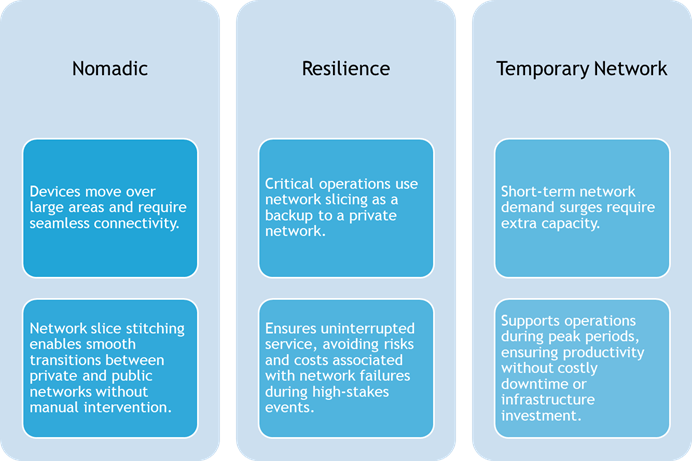
Figure 1 – Mixed deployment scenarios for enterprises
- Nomadic use cases
In nomadic use cases, devices or applications operate across a broad geographic area, requiring reliable connectivity beyond the confines of a single network. A prime example is the use of autonomous drones in port operations, where drones conduct inspections of infrastructure that would be challenging or time-consuming for human operators to access. In such scenarios, these drones utilize a public 5G network slice to coordinate real-time activities effectively. As the drones transition from the coverage of a private 5G network to the public network, seamless connectivity is critical.
To ensure this, enterprises rely on network slice stitching, a technology that allows devices to move effortlessly between network slices without manual intervention. This technology is gaining traction, with collaborations between leading operators and technology partners, piloting successful deployments that enable devices to operate across different operator slices. Slice mobility between different slices and operators may still face challenges in real-world applications, particularly when crossing geographic boundaries with varying coverage quality.
- Resilience use cases
For mission-critical applications, ensuring continuous operations is paramount. In such cases, enterprises may deploy network slicing as a redundancy mechanism alongside an existing private network. For instance, in a stadium setting, a private network may be used to guarantee high-quality, uninterrupted connectivity for broadcasting live sporting events. However, the risks and financial implications of a network failure, such as delays in live streaming, are substantial.
To mitigate these risks, enterprises can leverage a dedicated network slice from the public 5G network as a backup, ensuring seamless continuity in case of any disruption to the private network. This dual approach balances resilience and performance, particularly in environments where failure is not an option.
Failover mechanisms for such hybrid setups are still an evolving space. Seamless failover between private and public slices may depend on network orchestration maturity and real-time analytics capabilities.
- Temporary network use cases
Enterprises often face short-term surges in network demand that strain their existing infrastructure. During such periods, public 5G network slicing offers a cost-effective solution to augment capacity temporarily. For instance, during high-demand events (e.g., Amazon Prime Day), significant spikes in consumer demand place extraordinary pressure on warehouses and the broader supply chain. In such instances, a network slice can supplement a private 5G network to ensure seamless operations and minimize disruptions.
By leveraging a network slice during these peak periods, enterprises can maintain productivity and avoid the potential costs associated with downtime, ensuring they meet demand without overhauling their core infrastructure.
Managing Mixed Network Deployments
The successful deployment of mixed networks—where private networks and network slicing coexist—requires a unified, automated operational environment. This approach ensures seamless integration and management across service, network, and edge domains.
A robust solution will need to incorporate several orchestration functions and operational systems, such as configuration management, real-time inventory management, and assurance. Key components of this environment include:
- Intelligent resource placement across on-premises infrastructure, network edge, and cloud platforms. This capability is currently under development by leading operators, as they work to optimize resource allocation based on specific enterprise needs.
- Zero-touch deployment, provisioning, and configuration of hybrid services and network slices. As dynamic slicing matures over the next 1-2 years, this capability will become critical, enabling operators to offer agile, automated service setups.
- Continuous service and slice lifecycle management, which includes on-demand scaling, regular network updates without downtime, and self-healing mechanisms. These capabilities ensure that Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are consistently met, and network performance is continuously optimized.
To support these mixed deployment models, enterprises and operators alike must embrace new technologies in their deployment strategies. Traditional approaches will not suffice as hybrid environments become more complex and diverse.
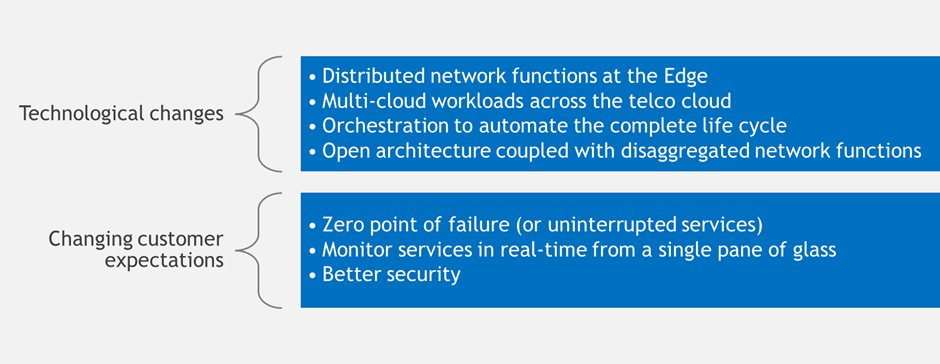
Figure 2 – Managing customer and technological changes
Ultimately, enterprise customers deploying a combination of private networks and network slicing are striving for specific connectivity outcomes. By leveraging these advanced orchestration tools and systems, they can achieve the tailored solutions necessary to meet the demands of their unique use cases, driving efficiency and unlocking new opportunities.
Conclusion
As the 5G ecosystem continues to evolve, CSPs must adapt to a landscape where multiple methods of network delivery coexist. Whether through network slicing or private 5G deployments, operators will need to tailor their networks to support enterprise decision-making.
With the rise of more complex enterprise networking demands, the role of orchestration solutions becomes pivotal in simplifying management, both today and in the future. Factors such as cell site positioning, spectrum allocation, scalability, and advanced analytics capabilities will drive the increasing adoption of network slicing within the public 5G domain.
Additionally, enterprises deploying Standalone Private 5G (P5G) networks can further benefit by running network slices on top of their infrastructure, unlocking even greater flexibility and value.
Tata Communications Transformation Services (TCTS) has taken a forward-thinking approach, acting as a service integrator that customizes solutions based on specific enterprise needs. By doing so, TCTS accelerates new service creation, enhances operational efficiency, and integrates diverse partners into the ecosystem, positioning itself as a key enabler in driving the next wave of 5G innovation.
References
[1] GSMA – Impact of Spectrum Set Asides on 5G
























![Telco Cloud: A Key Enabler to Telco Transformation [Part 1]](https://www.tatacommunications-ts.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Telco-Cloud-blog_image-1-500x383.png)




